Live Streaming Platform Architecture¶
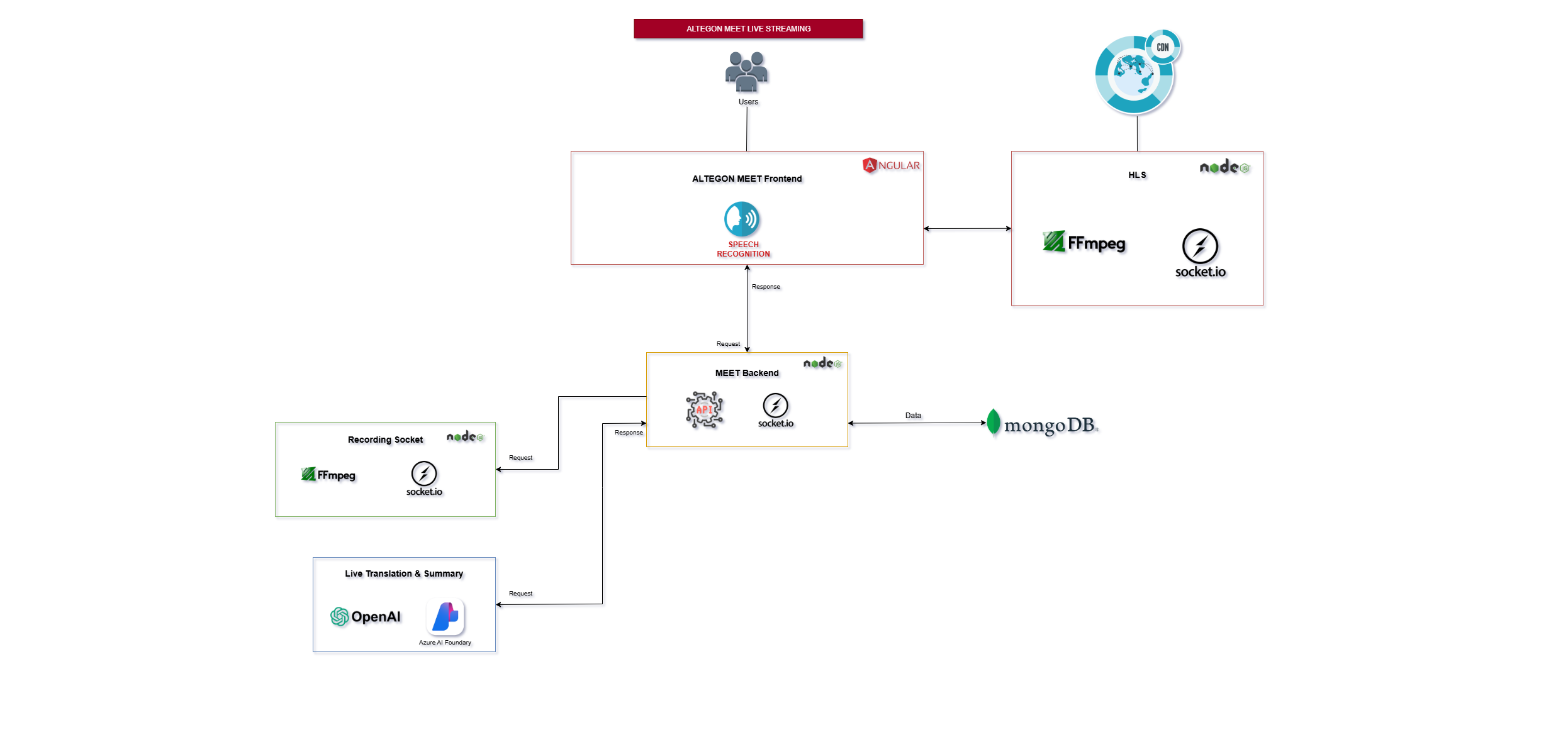
Architecture Overview¶
The Live Streaming Platform is a comprehensive one-to-many broadcasting solution that enables high-quality video streaming with real-time transcription, recording, and analytics capabilities. The architecture supports unlimited concurrent viewers worldwide through adaptive bitrate streaming, efficient segment-based delivery, and global CDN distribution.
System Components¶
Frontend Layer¶
The frontend provides distinct interfaces for different user roles with specialized functionality:
Broadcaster Interface¶
- Purpose: Control center for content creators and broadcasters
- Built With: Angular framework
- Key Features:
- Live Streaming Controls:
- Start/stop broadcast
- Camera and microphone management
- Speech Recognition Integration: Real-time transcription / captions of broadcaster's audio
- Role-Specific Controls: Broadcast settings and configurations
- MediaRecorder API: Captures video blobs from the broadcaster's stream
- Socket.IO Communication: Sends captured video blobs to HLS Server in real-time
Viewer Interface¶
- Purpose: Optimized playback experience for stream consumers
- Technology: Video.js library for robust video playback
- Key Features:
- Adaptive Streaming Playback: Buffer management for smooth playback
- Live Captions Display: Shows real-time transcriptions
- Interactive Controls:
- Play/pause (for recorded streams)
- Volume control
- Fullscreen mode
- CDN-Optimized Fetching: Retrieves video segments through CDN.
- Segment Fetching: Continuously fetches video segments from HLS server via URL requests
Backend Services¶
The backend manages all business logic, user sessions, and real-time communication:
REST API Endpoints¶
- Key Endpoints:
- Stream Management:
- Create stream sessions
- Stream configuration and settings
- Access control and authentication
- User Management:
- Broadcaster authentication and authorization
- Viewer access and permissions
- Role-based access control
- Analytics:
- Retrieve live streaming statistics
- Historical data queries like transcription etc.
Socket.IO Events¶
- Room Management:
- Create streaming rooms dynamically
- Manage broadcaster and viewer connections
- Handle room lifecycle (creation, destruction)
- Statistics Collection:
- Viewer Count: Real-time tracking of concurrent viewers
- Geographic Data:
- Viewer locations (city and country)
- Regional distribution analytics
- Connection Quality: Monitor stream health and viewer experience
- Event Broadcasting: Notify viewers of stream status changes
- Data Persistence: Store collected statistics to MongoDB
Database Layer¶
MongoDB¶
- Purpose: Centralized data storage for all platform data
- Stored Data:
- Session Information:
- Stream metadata
- Viewer Analytics:
- Total viewer count
- Geographic distribution data
- User Data:
- Broadcaster profiles and credentials
- Historical Records:
- Past stream sessions
- Transcription archives
Recording Server¶
A dedicated microservice responsible for video recording and processing:
Key Features:¶
- FFmpeg Integration:
- Processes incoming video blobs in real-time
- Creates video segments for efficient streaming
- Encodes final output to MP4 format
- Storage Management: Saves processed recordings to designated file paths
- Socket Communication: Send and Receives video blob data via Socket.IO events
- Processing Pipeline:
- Receives raw video blob from active meeting
- Processes and segments video using FFmpeg
- Creates optimized MP4 file
- Stores recording at configured storage location
Transcription & Summary Generation Component¶
An AI-powered service for generating meeting transcripts and summaries:
Transcription Service¶
- Technology: Azure AI Foundry Model
- Function: Converts spoken audio to accurate text transcription
- Features: Real-time transcription during meetings
Summary Generation¶
- Technology: OpenAI Model (GPT-based)
- Function: Analyzes complete transcription to generate concise meeting summaries
- Output: Meeting overview for quick review
HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) Server¶
The HLS Server is the core component that enables adaptive bitrate streaming:
Architecture:¶
- Technology: Node.js-based streaming server
- Protocol: HLS (HTTP Live Streaming)
- Communication: Dedicated Socket.IO connection with broadcaster frontend
- CDN Integration: Seamless integration with Content Delivery Network for global distribution
Key Functions:¶
1 Video Blob Reception
- Source: Receives video blobs from broadcaster's MediaRecorder via Socket.IO
- Real-time Processing: Handles incoming video data as a continuous stream
- Buffer Management: Efficiently manages incoming data to prevent memory issues
2 Segment Processing
- FFmpeg Integration: Processes video blobs into streaming segments
- Output Files:
- Manifest File (live.m3u8):
- Master playlist containing segment references
- Duration information for each segment
- Sequence numbers for proper playback order
- Updated continuously as new segments are created
- Video Segments (seg001.m4s, seg002.m4s, ...):
- Short duration video chunks (typically 2-10 seconds)
- FFMPEG format for broad compatibility
- Sequential numbering for ordered playback
- Optimized for HTTP delivery and CDN caching
3 CDN Integration & Content Delivery
Our platform supports Content Delivery Network (CDN) integration for optimal global streaming performance:
- Global Edge Distribution: Video segments cached at CDN edge servers worldwide
- Reduced Latency: Viewers fetch content from geographically nearest CDN node
- Bandwidth Optimization: Reduces load on origin HLS server
- Scalability: Handles millions of concurrent viewers without origin server strain
- High Availability: CDN redundancy ensures stream availability even during server issues
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces origin server bandwidth costs through edge caching
Data Flow Architecture¶
Complete Streaming Workflow:¶
Phase 1: Stream Initialization¶
- Broadcaster Login: Authentication via REST API
- Stream Setup: Creates stream session through backend
- Socket Connection: Establishes WebSocket connection for real-time communication
- Room Creation: Backend creates streaming room and notifies components
- Database Entry: MongoDB stores initial session metadata
- CDN Configuration: CDN endpoints configured for stream delivery
Phase 2: Live Broadcasting¶
- Media Capture: Broadcaster's MediaRecorder captures video/audio
- Dual Transmission:
- Path A (Live Streaming):
- Video blobs → Socket.IO → HLS Server
- HLS Server processes blobs with FFmpeg
- Creates live.m3u8 + seg00X.m4s files
- CDN Upload: Segments pushed to CDN origin automatically
- CDN Replication: Content replicated to edge servers globally
- Serves segments via HTTP (origin or CDN)
- Path B (Recording):
- Video blobs → Recording Socket → Recording Server
- FFmpeg processes and stores as MP4
- Transcription: Azure AI processes audio for live captions. These transcriptions are send to viewer using socket events.
- Viewer Access:
- Video.js requests manifest from CDN/origin
- Continuously fetches segments from nearest CDN edge
- Adaptive quality based on network conditions
Phase 3: Viewer Experience¶
- Join Stream: Viewer accesses stream URL
- CDN Routing: Automatically directed to nearest CDN edge server
- Manifest Request: Video.js fetches live.m3u8 from CDN (or origin if CDN cache miss)
- Segment Fetching:
- Continuous HTTP requests for latest .m4s segments
- Served from CDN edge cache (low latency)
- Falls back to origin if needed
- Caption Display: Real-time transcription shown if enabled
- Statistics Update: Backend logs viewer connection (location, count, duration)
Phase 4: Post-Stream Processing¶
- Stream End: Broadcaster stops streaming
- Final Segments: HLS Server processes remaining blobs
- CDN Final Push: Last segments uploaded to CDN
- Recording Finalization: Recording Server completes MP4 file
- Summary Generation: OpenAI analyzes transcript and creates summary when user clicks the generate summary button on dashboard page
- Analytics Storage: Complete session statistics stored in MongoDB
- Content Available: Recorded stream ready for on-demand viewing
- CDN Cache Optimization: Popular recordings kept in CDN cache longer
HLS (HTTP Live Streaming)¶
What is HLS?¶
HLS is an adaptive bitrate streaming protocol developed by Apple that breaks video into small HTTP-based file segments, allowing: - Universal Compatibility: Works on all modern browsers and devices - Adaptive Streaming: Automatically adjusts quality based on network speed - CDN Friendly: Uses standard HTTP, easily cached and distributed globally - Firewall Friendly: Uses port 80/443, no special ports needed
HLS Components:¶
1. Manifest File (.m3u8)¶
- Plain text playlist file
- Lists all available video segments in order
- Contains metadata (segment duration, sequence number, encryption info)
- Updated in real-time during live streams
- Example structure: #EXTM3U #EXT-X-VERSION:3 #EXT-X-TARGETDURATION:10 #EXTINF:10.0, seg001.m4s #EXTINF:10.0, seg002.m4s
2. Video Segments (.m4s or .ts)¶
- Short video chunks (typically 1-10 seconds)
- Can be cached by CDN for efficient delivery
- Independently playable
HLS Workflow in Our Platform¶
- Capture: MediaRecorder captures broadcaster's stream
- Transmission: Blobs sent via Socket.IO to HLS Server
- Segmentation: FFmpeg processes blobs:
- Output: Generates live.m3u8 and seg00X.m4s files
- CDN Upload: Segments automatically pushed to CDN origin
- Edge Replication: CDN replicates to global edge servers
- Delivery: Files accessible via CDN URLs for low-latency global access
- Playback Video.js player:
- Fetches live.m3u8 from nearest CDN edge every few seconds
- Downloads new segments from CDN cache
- Plays segments sequentially
- Switches quality if network changes
API Documentation¶
For detailed REST API endpoints, authentication methods, and integration guides, please refer to the Live Streaming API Documentation page.
Support & Contact¶
For technical implementation assistance, troubleshooting, or additional architecture details, please contact our support team.